Important Guidelines
- Provide your Export Control Classification Number (ECCN) and United Nations Standard Products and Services Code (UNSPSC) in your pricing page on IBM Partner Center.
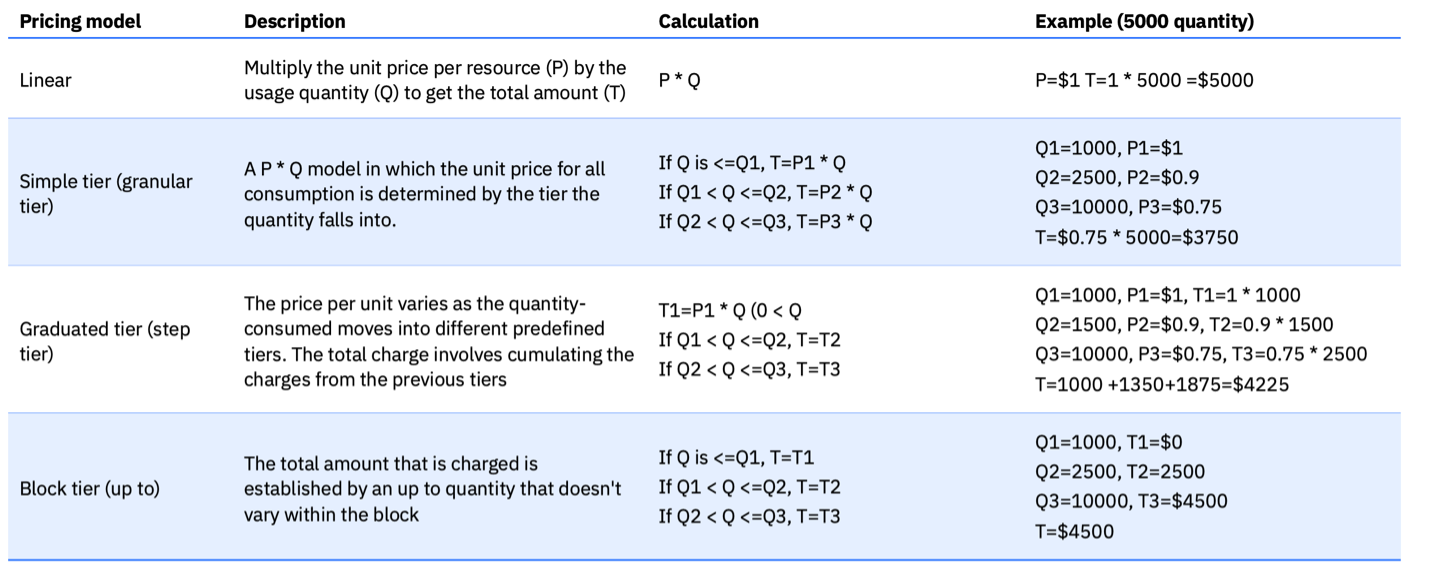
Simplified Calculation
- Price: Amount the customer pays per unit of usage
- Quantity: Metering unit that determines how usage is measured
Pricing Models
watsonx Orchestrate Partner Agent Price Plans and Metering
To enable sales, customer purchases, and billing for partner agent services, partners must register their agent offerings in the IBM Cloud Catalog. As part of onboarding, partners must define price plans and usage metrics for their agents. The IBM Cloud Catalog primarily supports traditional SaaS offerings, where metering typically revolves around service instances, users, or resource consumption. However, wxO partner agents—especially those involving AI/ML and agentic workflows—require a different approach to usage tracking. For wxO, usage should be measured in terms of agent activity, AI/ML-driven outcomes, or task-based execution rather than conventional SaaS metrics. Partners should design metering models that reflect the unique value delivered by intelligent agents.Designing Your Price Plan and Usage Metrics
Define metrics that reflect how your agents operate and deliver value. Common examples:- Messages: Number of discrete messages exchanged between the agent and users, systems, or other agents.
- Active User: Unique users who engage with the agent over a defined period (typically monthly).
- Monthly Active Users (MAU): Unique users interacting with the agent during a calendar month.
- Voice MAU: Unique users interacting via voice channels (e.g., IVR, smart assistants, telephony).
- Document: A distinct file or knowledge artifact processed, generated, or retrieved by the agent.
- Event: A Tool Run, meaning the execution of a Tool within an agent.
- A Tool may be a single action (e.g., add a row to a table) or a multi-step action (e.g., find contacts, create a table, send an email).
- If multiple tools run in sequence (a tool flow), each Tool Run counts as a separate Event.
- Tool Runs in preview mode (testing before publishing) do not count toward consumption.
Pricing Models and Metrics
Agent services can be priced in different ways:-
Fixed Plan (Agent-Oriented):
Flat monthly fee for unlimited agent access.
Example: One fixed fee per customer for unlimited usage each month. -
Usage-Based Plan:
Pricing tied to actual usage (messages, documents, or events).
Example: A customer pays a set fee for every 100 messages exchanged. -
Hybrid Plan (Fixed + Usage-Based):
Combines a base fixed fee with incremental charges for extra usage.
Example: A fixed monthly fee includes 5,000 messages. Each additional 100 messages costs X dollars.
Detailed Walk-through: Creating Agent Price Plan and Metrics
- Log in to IBM Cloud and go to Partner Center → My Products.
- In the left-hand panel, click Pricing.
- Enter your ECCN and UNSPSC.
-
In the Pricing Plan section, click Add Plans and configure based on your business needs.
- Example: Create a usage-based plan.
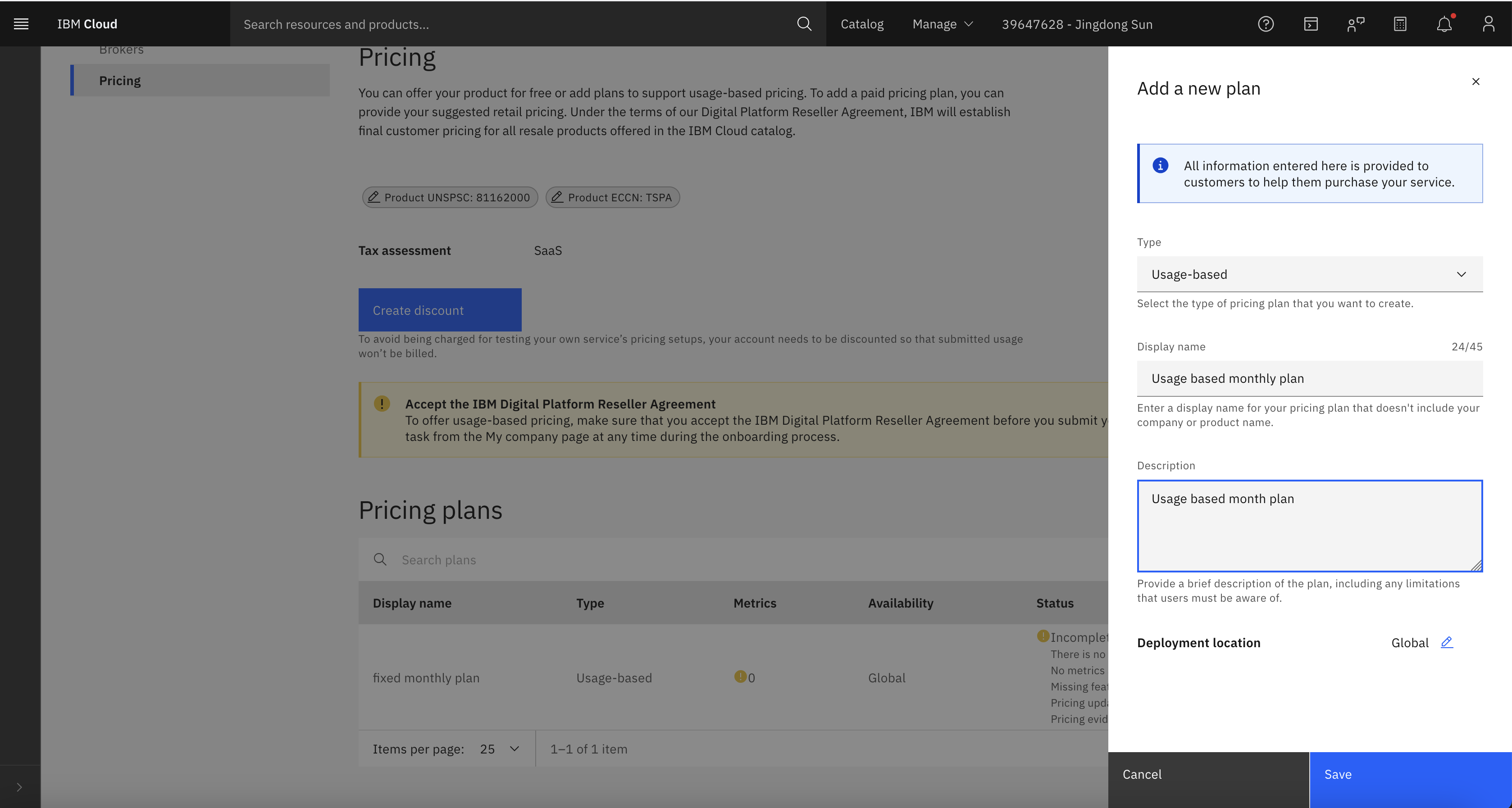
-
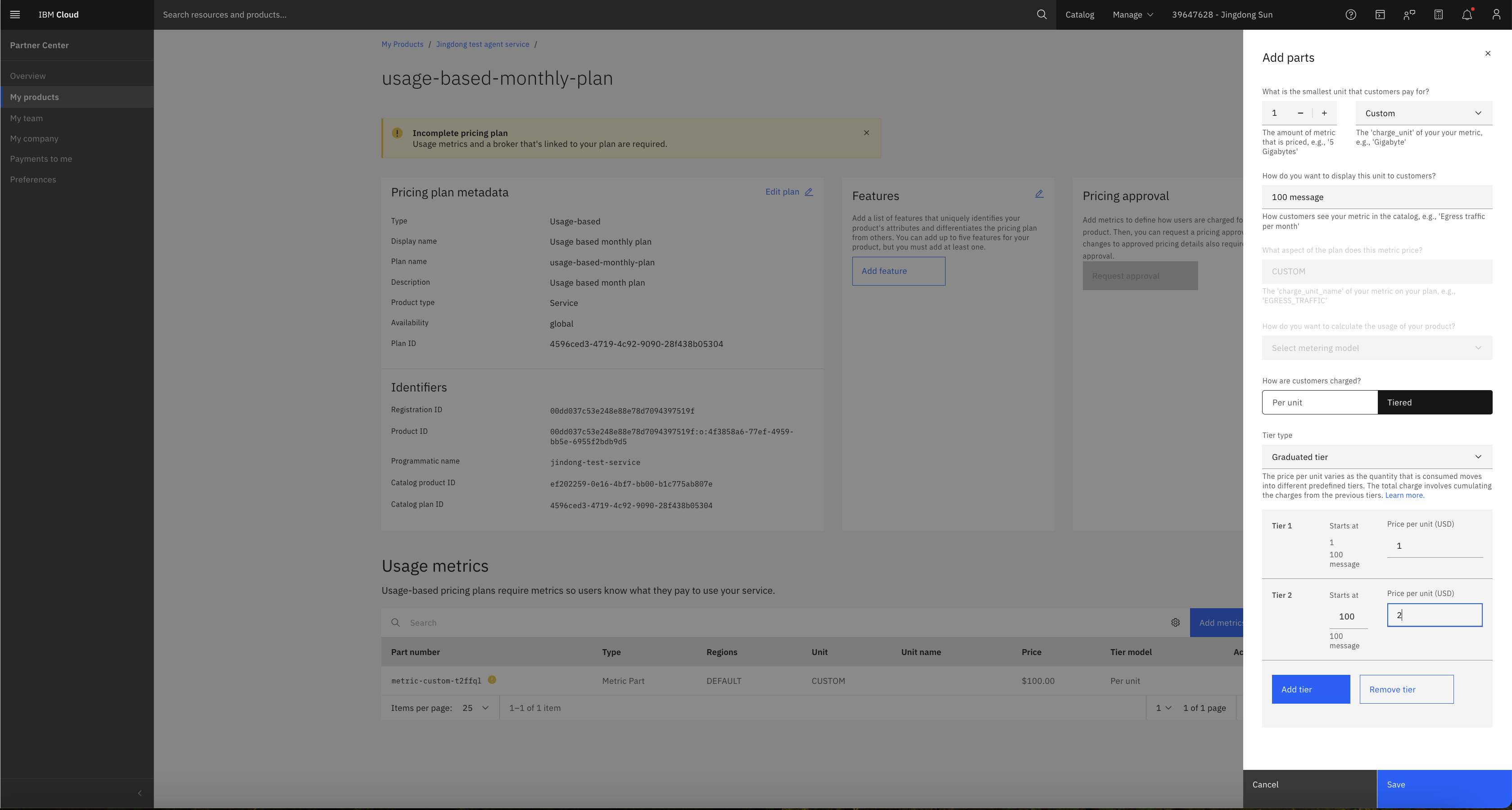
Click the pricing plan and click Add metric.
-
You can create a Usage-based metric:
-
You can also create a fixed metric:
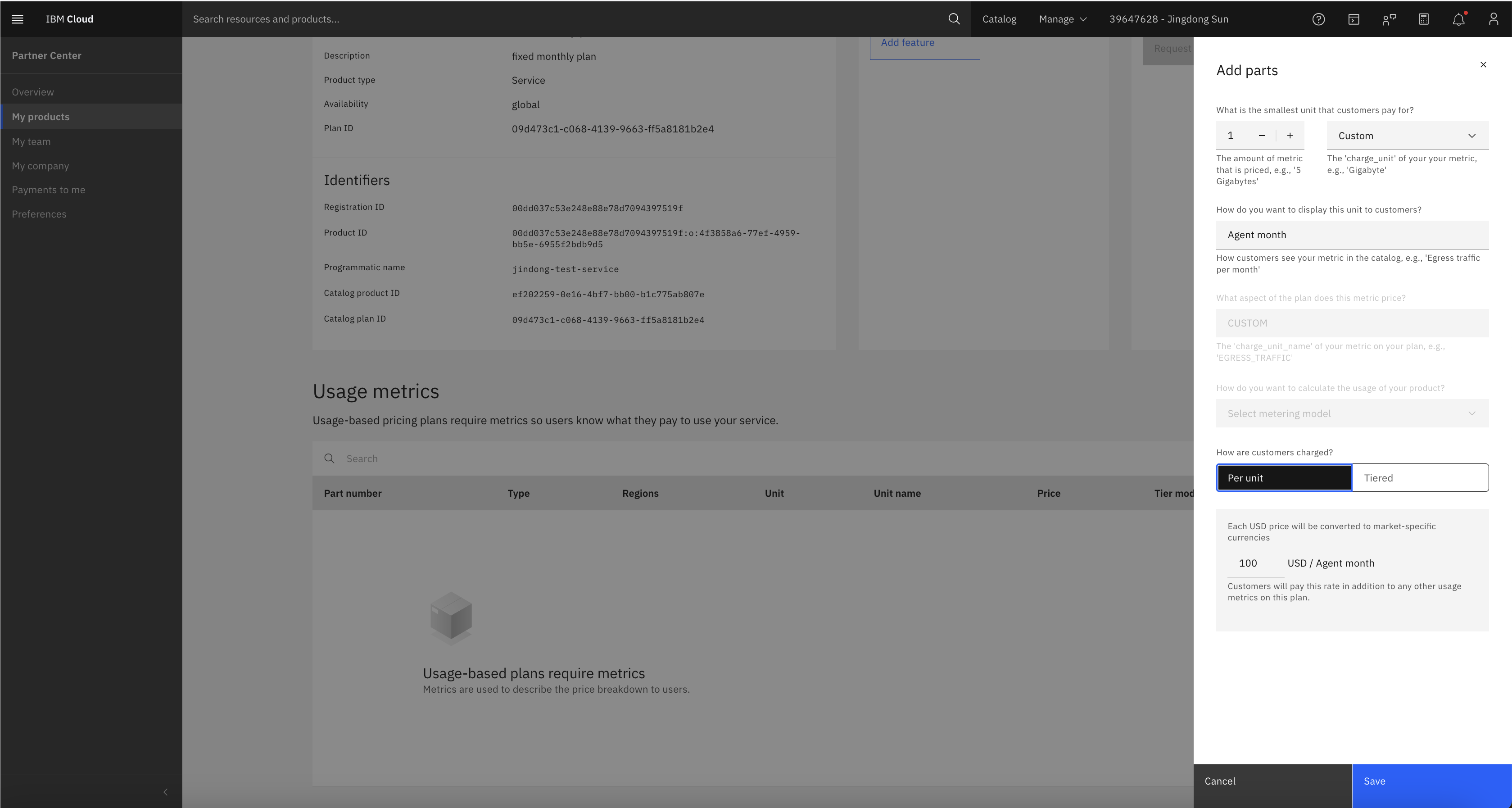
-
You can create a Usage-based metric:

